



Next: Cardinal B-Splines
Up: Specific problem
Previous: Ewald
Contents
PME
An operation called Fast Fourier Transform exists that can perform the required Fourier Transform much faster,
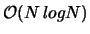 . The problem is that a Fast Fourier Transform can only be performed on a function that is defined on a regularly spaced grid. Because the position of the charges in our cell is not regular it is not initially feasible to use FFTs. Another technique, first proposed by Tom Darden in [7], called Particle Mesh Ewald (PME) solves this problem. In this technique, Darden used an interpolating function to assign pieces of the charges to a regularly spaced mesh that could be operated on by a Fast Fourier Transform. This adds additional overhead, but all of the new operations are
. The problem is that a Fast Fourier Transform can only be performed on a function that is defined on a regularly spaced grid. Because the position of the charges in our cell is not regular it is not initially feasible to use FFTs. Another technique, first proposed by Tom Darden in [7], called Particle Mesh Ewald (PME) solves this problem. In this technique, Darden used an interpolating function to assign pieces of the charges to a regularly spaced mesh that could be operated on by a Fast Fourier Transform. This adds additional overhead, but all of the new operations are
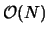 or less, the overall technique is
or less, the overall technique is
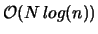 which is a significant improvement over the conventional Ewald. We used an adaptation of the PME method, suggested in [9]. This uses an alternative interpolating function, called Cardinal B-Splines which are more accurate and differentiable.
which is a significant improvement over the conventional Ewald. We used an adaptation of the PME method, suggested in [9]. This uses an alternative interpolating function, called Cardinal B-Splines which are more accurate and differentiable.
Subsections
Thomas G Dimiduk
2004-04-15