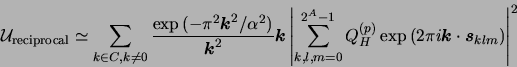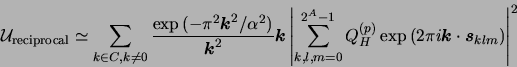Next: Background Research
Up: Equations
Previous: Ewald Equations
Contents
The PME method replaces the reciprocal term with another set of equations that are lower-order. The direct replacement for
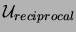 is:
is:
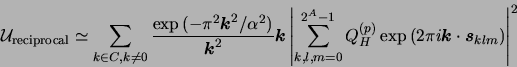 |
(7) |
11.
This depends on the charge mesh
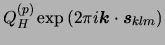 , and the sum over
, and the sum over 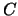 indexes over all mesh points. The mesh function is calculated calculated using 8
indexes over all mesh points. The mesh function is calculated calculated using 8
where 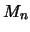 is the Cardinal B-Spline of order n given by the recursive function:
is the Cardinal B-Spline of order n given by the recursive function:
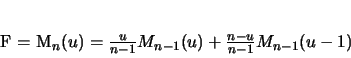 |
(8) |
and, for any real number, 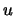 ,
,
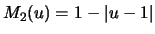 for
for
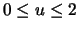 and
and 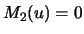 for
for 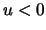
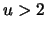 12
The PME reciprocal space term, see Appendix A.5: recpTerm.F for code, calculates the reciprocal contribution using the Particle Mesh Ewald Method as discussed earlier in Section 2.3.
12
The PME reciprocal space term, see Appendix A.5: recpTerm.F for code, calculates the reciprocal contribution using the Particle Mesh Ewald Method as discussed earlier in Section 2.3.
Thomas G Dimiduk
2004-04-15